Below is a narrated animation about BPH and treatments. Click here to license this video on Alila Medical Media website.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or enlarged prostate, is a condition in which the size of the prostate gland is increased. It is considered “benign” because it’s NOT a cancer, and it does not increase the risk of cancer. However, when becomes sufficiently large, the prostate tissue may compress the urethra and block the urine flow causing a number of urination problems and urinary tract infection. BPH is very common in aging men: about 50% of men have some degree of BPH by the age of 60.
Anatomy
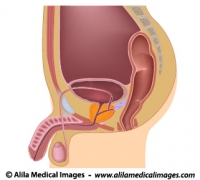
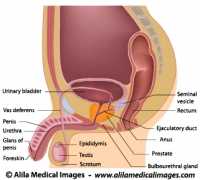
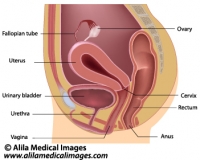
The prostate is a walnut-size exocrine gland of the male reproductive system. It is located just below the urinary bladder where it wraps around the first part of the urethra – prostatic urethra (see Fig. 1 and 2).

Fig. 1: Male reproductive and urinary organs, mid-sagittal view. Click on image to see a larger version on Alila Medical Media website where the image is also available for licensing.
Prostate gland produces a milky fluid that is expelled into the urethra to mix with spermatozoa during ejaculation. The fluid serves as a lubricant and nutrition for the sperms.
Click here to see an animation of male reproductive system on Alila Medical Media website where the video is also available for licensing.
Click here to see an animation of male urinary system on Alila Medical Media website where the video is also available for licensing.
In BPH, the enlarged prostate presses on the prostatic urethra making it narrower. This affects normal flow of urine (Fig. 2).

Fig. 2: Normal prostate (left) and enlarged prostate (right). Same sagittal view as in Fig. 1 with other organs removed to simplify. The urethra is squeezed narrow in BPH. Click on image to see a larger version on Alila Medical Media website where the image is also available for licensing.
Click here to see an animation of prostate hypertrophy on Alila Medical Media website where the video is also available for licensing.
Causes
BPH is considered a normal part of male aging as a result of hormonal changes. The rate of cell proliferation induced by androgens (male hormones) somehow exceeds the rate of programmed cell death (apoptosis) in aging prostate tissue resulting in enlargement of the prostate.
Severity of BPH (development of symptomatic BPH), however, has been associated with lifestyle. The incidence of clinically significant BPH is notably higher in men who lead a modern lifestyle compared to those who live in rural traditional settings.
About half of men with histopathologic BPH demonstrate clinically significant symptoms.
Symptoms
Obstruction of urine flow makes urine voiding difficult and incomplete. This leads to common symptoms of BPH:
– frequent urination.
– urgency : need to void that can not be deferred.
– urinary hesitation: difficulty to initiate urine stream, weak and interrupted stream.
– straining to void: need to push to completely empty the bladder.
– residual urine: constant feeling of need to void.
– dribbling
Altogether the voiding dysfunction resulted from BPH is called lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) – a more recent term for prostatism.
Treatment
Patients with mild symptoms and who are not bothered by their symptoms are usually advised to follow a “watch and see” approach with regular check-up and lifestyle changes such as low-fat diet, reduced consumption of alcohol and caffeine, reduced fluid intake before bedtime, avoidance of certain products and medications such as diuretics,…
1. Medication
There are two main classes of medication:
– alpha-blockers: these drugs relax smooth muscle in the prostate and by doing so relieve blockage of urine flow.
– 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: these inhibit local production of the hormone that is responsible for prostate enlargement.
2. Minimal invasive treatment
These non-surgical therapies use heat to cause cell death (necrosis) in prostate tissue. The heat is delivered in small amount and to a specific location to minimize unwanted damage. Different procedures differ mainly in the type of energy used.
– Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT): use of microwave energy delivered through a probe inside a catheter inserted into the urethra.
– Transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) : use of radio frequency energy delivered through a transurethral device with needles.
– Photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP): use of laser to vaporize prostate tissue.
3. Surgery
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure for removal of prostate tissue through the urethra. This procedure has been around for a long time and is still considered gold standard for treatment of severe BPH. Nowadays, it is usually performed when medications and less invasive methods fail.
See all Urology topics