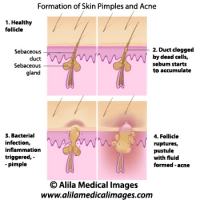
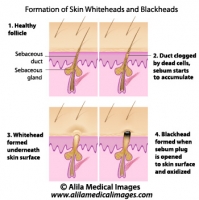
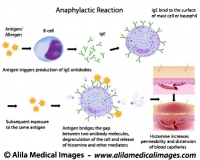
The following video is available for licensing on Alila Medical Media website. Click here!
What is cellulite?
Cellulite is the dimpling, lumpy appearance of the skin, commonly occurs in females after puberty age. It’s most visible on the thighs, the buttocks, and belly. Other names include adiposis edematosa, dermopanniculosis deformans, status protrusus cutis, gynoid lipodystrophy, orange peel syndrome and cottage cheese skin. Cellulite is not a disease and should NOT be confused with cellulitis, which is the infection of skin and underlying tissues.
Anatomy of cellulite
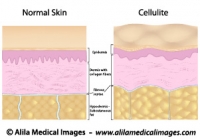
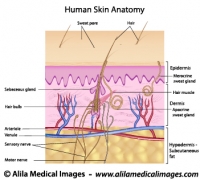
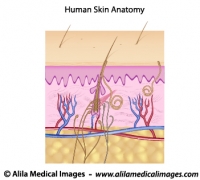
The skin has three layers : epidermis (outermost), dermis and subcutaneous fat (Fig.1). Vertical bands of connective tissue called fibrous septae (singular: septum) connect the dermis to underlying soft tissues. Cellulite happens when fat cells accumulated in the subcutaneous fat layer push the skin up while the fibrous septae pull it down. These two actions in opposite directions result in the bumpy appearance of the skin. In people with thin skin, this becomes even more noticeable.

Fig. 1 : Structure of normal skin and skin with cellulite, back to back for comparison. Note the fibrous septae pull the skin down in cellulite. Click on image to see a larger version on Alila Medical Media website where the image is also available for licensing.
Causes
Causes of cellulite are not fully understood but the following factors are likely to be involved:
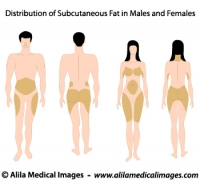
– Hormonal : Over 80% of women over the age of 20 has some degree of cellulite. Cellulite is rare in men, but is more common in those with androgen deficiency.
– Genetic: Some genetic make-ups are likely to be predisposing factors. You have more chance of getting it if other women in the family have it.
– Lifestyle: Diet and exercises definitely have a good share of contribution. Reducing body fat typically improves cellulite appearance. Extreme diet, however, may produce adverse effect as thinner skin makes it more visible (see the anatomy part above).
Treatment
Various therapies are available including massages, heat therapy, ultrasound, drugs,… These treatments supposedly act to either reduce subcutaneous fat or thicken the skin, but none are scientifically proven to be effective in the long term.
The latest technology based on releasing of the fibrous septae that pull the skin down (see the anatomy section above) has received a better response from scientists. Cellulaze, a device that uses laser beams to cut through the fibrous septae, has produced promising initial results in U.S. clinical trials. It’s been advised, however, to take this approach with precaution given the newness of the technique and shortness of long term data.
Finally, as repetitive and obvious as it may sound, the best treatment for cellulite is to maintain a healthy lifestyle, eating healthy (but no extreme diet), drinking lots of fluid and daily exercises.